RFID is a technology for identifying objects using radio waves that are being widely applied in many industries, fields of management, and inventory storage. So, do you fully understand what RFID is, its principles, operating frequencies, applications, and more? Let's explore the answers together with Thai Tuan LMS in the article below.

What is RFID?
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification) is an automatic identification technology that uses radio frequency waves to read and identify information from RFID tags attached to various objects.

The advantage of RFID is its ability to read and retrieve data without direct contact and to operate effectively in various materials such as fabric, concrete, fog, paint, cardboard, and other challenging environmental conditions.
What does an RFID system consist of?
An RFID system is composed of two main components:
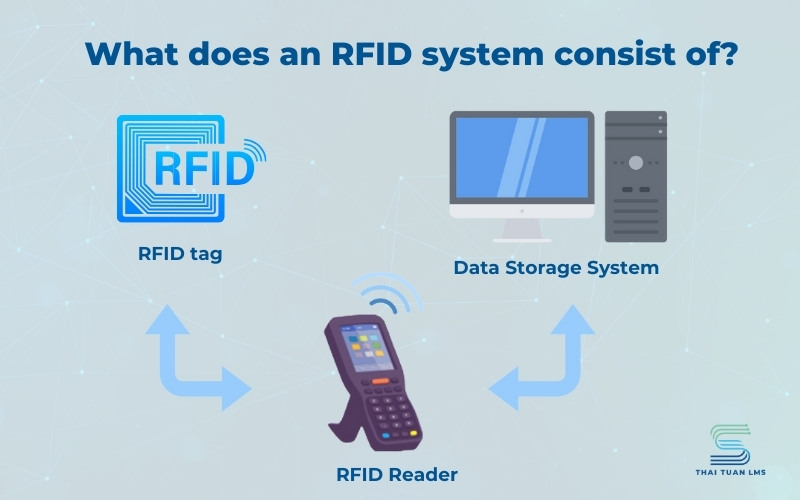
RFID Tag: A small device that contains a chip and an antenna for transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves, attached to the object to be tracked.
There are two types of RFID tags:
- Passive tags: Do not require an external power source and derive energy from the reader. They have a short reading range.
- Active tags: Powered by a battery, allowing for a longer reading range.
RFID Reader: A device that emits radio waves to activate the RFID tag and collect data from it. The RFID reader can be connected to a computer for data processing and analysis.
In addition to these two main components, an RFID system may also include:
Antenna: A device that serves as a link between the tag and the reader. The reader emits signals to activate and communicate with the tag.
Server: Responsible for receiving, processing data, and providing monitoring, statistics, control, etc.
The working principle of RFID technology
The principle of operation of RFID technology is as follows:
- Activation: The RFID reader emits electromagnetic waves at a certain frequency to the RFID tag.
- Data Transmission: The RFID tag within the active range detects these electromagnetic waves, collects energy from them, and then transmits its data back to the RFID reader, revealing its identification number.
- Data Processing: The RFID reader collects data from the tag and transmits it to software on a computer or mobile device.
- Data Analysis: The computer processes and analyzes the data, returning the results collected from the RFID tag.
Operating Frequencies of RFID
The operating frequency of RFID is an important factor that affects the reading range, reading speed, and penetration capability of the RFID tag. RFID operates on the following frequency bands:
Low Frequency (LF)
- Frequency: 30 kHz - 500 kHz, typical frequency is 125 kHz
- Reading range: 10 cm - 2 meters
- Reading speed: Slow
- Penetration capability: High (can penetrate water, metal)
- Applications: Livestock tracking, waste management, access control
High Frequency (HF)
- Frequency: 3 MHz - 30 MHz, typical frequency is 13.56 MHz.
- Reading range: 10 cm - 1 meter
- Reading speed: Medium
- Penetration capability: Medium (can penetrate water, thin metal)
- Applications: Payment cards, access cards, library cards, asset tracking
Ultra High Frequency (UHF)
- Frequency: 300 MHz - 3 GHz, typical frequency is 433 MHz.
- Reading range: Can typically be read from over 750 cm.
- Reading speed: Fast
- Penetration capability: Low (difficult to penetrate water, metal)
- Applications: Warehouse management, supply chain, traffic control, luggage tracking
Super High Frequency (SHF)
- Frequency: 3 GHz - 30 GHz
- Reading range: Up to 100 meters
- Reading speed: Fastest
- Penetration capability: Very low (difficult to penetrate water, metal)
- Applications: Radar, satellites
Choosing the appropriate RFID frequency depends on various factors, including the application, operational environment, and materials to be tracked. Next, let’s continue exploring the applications of RFID with Thai Tuan LMS.
Applications of RFID
RFID technology is increasingly being applied in various fields and industries due to its ability to automatically identify and track information effectively. Notable applications of RFID include:

Supply Chain Management
- Tracking the location and status of goods throughout the transportation, storage, and distribution process.
- Minimizing loss of goods due to theft or misplacement.
- Optimizing warehouse management processes, enhancing operational efficiency.
Warehouse Management
- Monitoring the location, quantity, and condition of goods in the warehouse.
- Streamlining warehouse management processes and reducing losses.
Asset Management
- Tracking the location and condition of assets such as machinery, equipment, and vehicles.
- Preventing unauthorized use of assets.
- Automating maintenance and servicing processes.
Access Control
- Managing access at entry points to buildings, offices, and restricted areas.
- Monitoring employee working hours.
- Enhancing security and protection.
Electronic Payment
- Automatic payment at stores, toll booths, and subway ticket machines.
- Increasing speed and convenience for customers.
- Reducing payment fraud.
Healthcare
- Tracking the location and condition of patients and medical records.
- Managing medications and medical equipment.
- Enhancing treatment and patient care efficiency.
Retail Industry
- Monitoring inventory levels and preventing theft.
- Improving shopping experience for customers.
- Automating payment processes.
Textile Industry
- Tracking the production process, from raw materials to finished products.
- Combating counterfeit goods.
- Enhancing production management efficiency.
Animal Husbandry
- Tracking the location and status of livestock and poultry.
- Managing vaccinations and disease prevention.
- Improving farming productivity.
Sports
- Recording competition times and athletes' achievements.
- Preventing cheating in competitions.
- Enhancing professionalism in sports events.
Entertainment Industry
- Managing entry tickets to amusement parks.
- Processing payments for entertainment services.
- Tracking the location of children in play areas.
With the development of Industry 4.0, RFID technology is increasingly being implemented in various management fields due to its high accuracy, ability to operate in harsh environments without direct contact. RFID is gradually becoming an indispensable technology in modern life.
Comparison of RFID and Other Data Transmission Technologies
Currently, besides RFID technology, there are several other data transmission technologies such as barcode, NFC, and Bluetooth. Let's explore how these technologies differ.

|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Each technology has its own features and applications. The choice of technology depends on specific needs and objectives.
Advantages and Disadvantages of RFID Technology
In summary, the advantages and disadvantages of RFID can be seen as follows
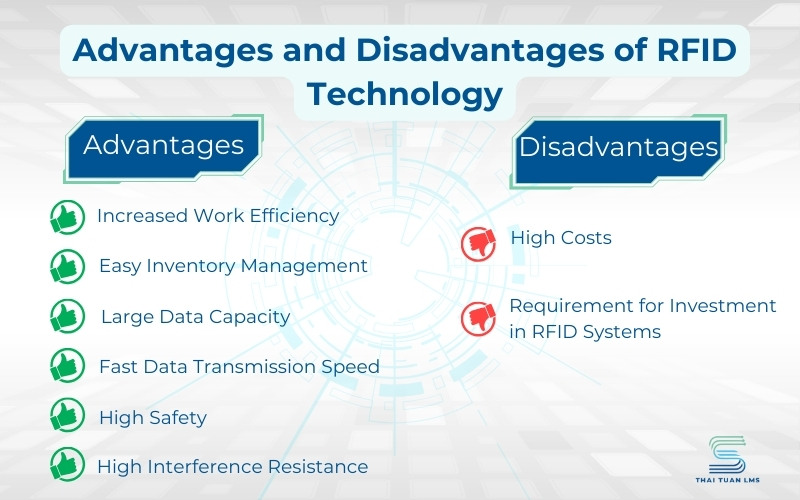
Advantages of RFID
- Increased Work Efficiency: RFID automatically identifies and tracks information without the need for direct contact, functioning even in harsh environments, thus saving time and effort while enhancing operational efficiency.
- Easy Inventory Management: The application of RFID in manufacturing helps automate traditional manual tasks, allowing for quick, detailed, and comprehensive tracking, retrieval, inspection, and reporting of inventory quantities.
- Large Data Capacity: RFID can store a larger volume of data compared to other data transmission technologies like barcodes.
- Fast Data Transmission Speed: RFID has a rapid data transmission speed, enabling quick and efficient data reading.
- High Safety: RFID offers high security, making it difficult to counterfeit or duplicate data.
- High Interference Resistance: RFID has a high resistance to interference, allowing it to operate effectively in noisy environments.
Disadvantages of RFID
- High Costs: The investment cost for an RFID system is higher than that of other data transmission technologies such as barcodes.
- Requirement for Investment in RFID Systems: To use RFID, investment is needed in RFID systems, including RFID tags, RFID readers, and management software.
RFID technology is one of the data transmission technologies with many superior features, high accuracy, and high operational efficiency in various environments and applications across many industries, making it a current trend in management technology.
At Thai Tuan LMS, we are applying smart RFID identification technology in laundry and linen management. The application of RFID in linen management will help businesses monitor real-time inventory levels, laundry status, and delivery status of linens, significantly reducing losses, costs, and operational time for the business.

The above is all the information that Thai Tuan LMS has compiled about what RFID is, its operating principles, applications, etc. We hope this information will be useful to you!

 Vietnamese
Vietnamese  English
English 










